Best RemoteIoT Behind Router For Raspberry Pi: Your Ultimate Guide
Are you tired of struggling with connectivity issues when setting up IoT devices behind a router? Well, buckle up because we’re diving deep into the world of remote IoT solutions tailored specifically for Raspberry Pi enthusiasts. In this article, we’ll uncover the best remote IoT setups that can seamlessly work even when your device is tucked behind a router. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a seasoned developer, this guide will equip you with everything you need to know.
Nowadays, IoT devices have become a staple in homes and businesses alike. However, one of the biggest challenges faced by users is ensuring their devices remain accessible remotely without compromising security. This is where Raspberry Pi comes in—a powerhouse of innovation that can handle complex tasks while maintaining affordability.
In this article, we’ll explore the best practices for setting up remote IoT systems behind a router using Raspberry Pi. From understanding the basics to advanced configurations, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s jump right in and discover how you can unlock the full potential of your Raspberry Pi for remote IoT applications.
Read also:Olsen Twins Fashion Lines A Complete Style Evolution You Need To Know
Why Raspberry Pi is the King of RemoteIoT
Let’s start with the basics. Why is Raspberry Pi such a game-changer in the world of remote IoT? The answer lies in its versatility, affordability, and ease of use. This tiny yet mighty device can handle everything from simple home automation to complex industrial applications. Plus, with its robust community support and endless resources, it’s no wonder why Raspberry Pi has become the go-to choice for developers worldwide.
Here are a few reasons why Raspberry Pi is perfect for remote IoT:
- Compact Size: Small enough to fit anywhere, yet powerful enough to handle heavy-duty tasks.
- Affordable: You don’t need to break the bank to get started with Raspberry Pi.
- Flexible: Supports a wide range of operating systems and programming languages.
- Community Support: A vast network of developers and enthusiasts ready to help you troubleshoot and innovate.
So, whether you’re looking to build a smart home system or a remote monitoring solution, Raspberry Pi has got your back.
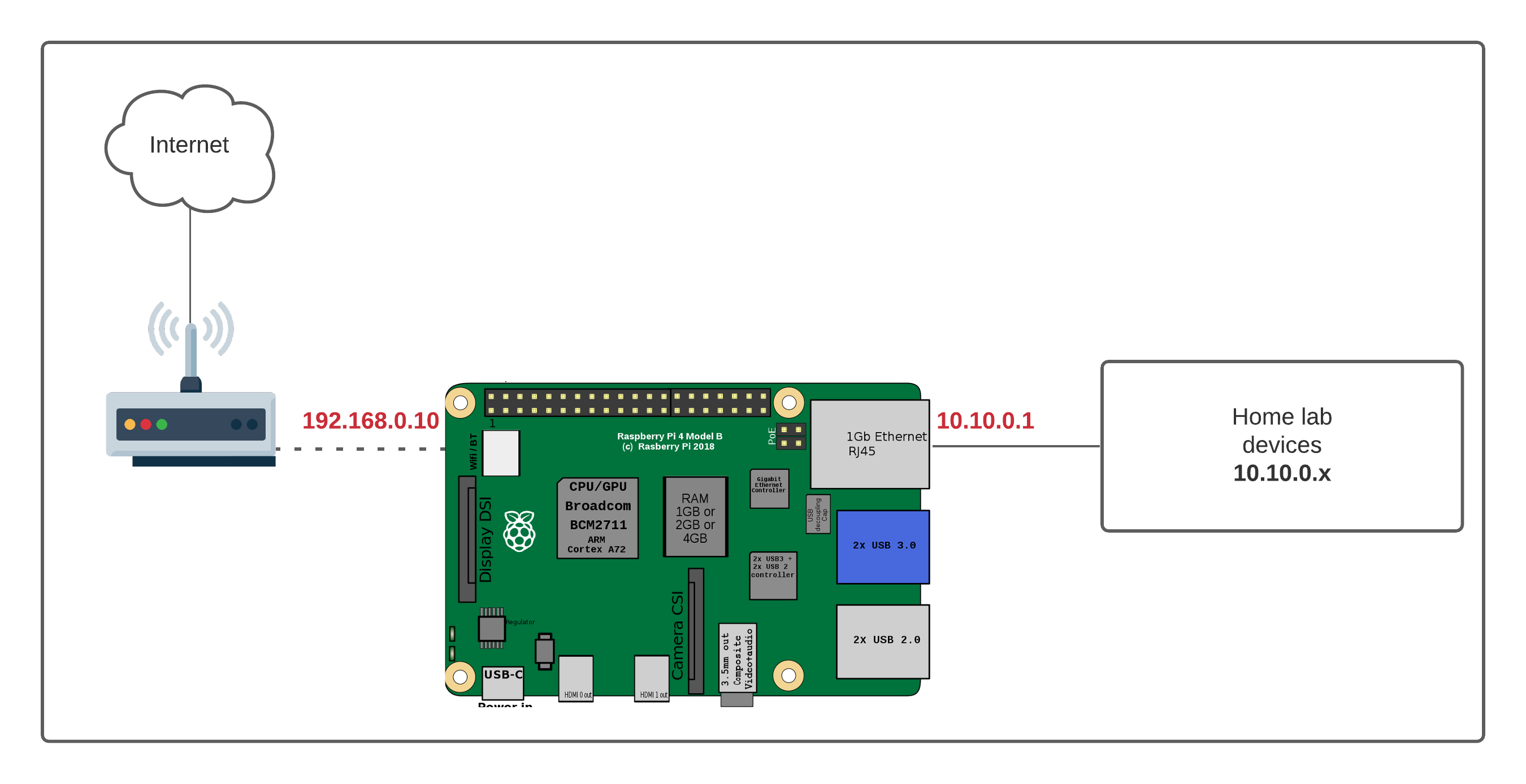
Understanding RemoteIoT Behind a Router
When it comes to IoT devices, connectivity is king. However, setting up remote access for devices behind a router can be a bit tricky. This is because routers act as a barrier, protecting your network from unauthorized access. While this is great for security, it can pose challenges for remote IoT setups.
Key Challenges in RemoteIoT
Here are some common challenges you might face when setting up remote IoT devices behind a router:
Read also:Breaking News Dwayne And Gabrielle Divorce 2024 Ndash A New Chapter Unfolds
- Firewall Restrictions: Routers often come with built-in firewalls that block incoming connections.
- Dynamic IP Addresses: Most home routers use dynamic IP addresses, making it difficult to establish a stable connection.
- Port Forwarding: Configuring port forwarding can be complex and may not always work as expected.
Don’t worry though, because we’ve got some awesome solutions to help you overcome these challenges. Keep reading to find out more!
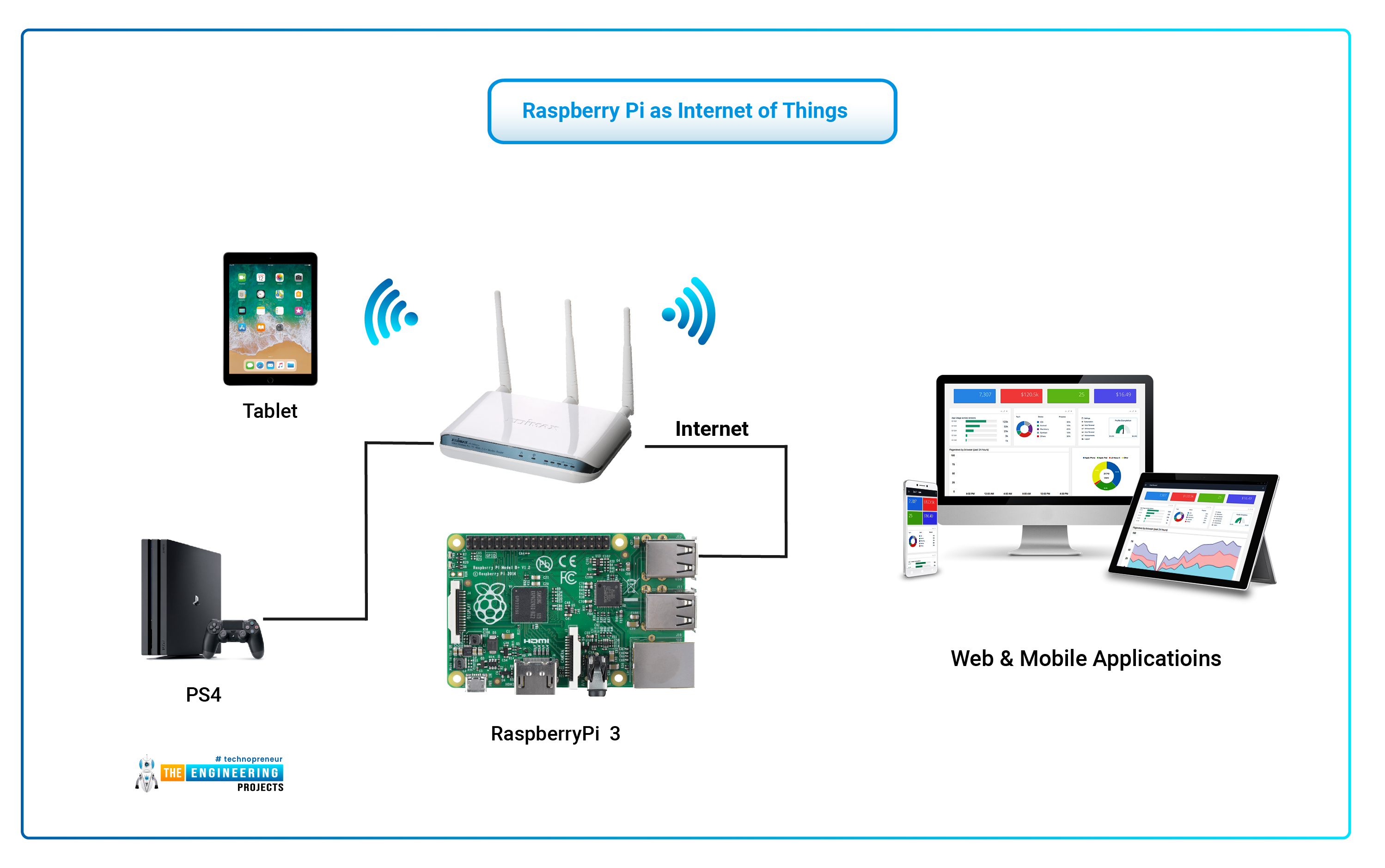
Top RemoteIoT Solutions for Raspberry Pi
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dive into some of the best remote IoT solutions for Raspberry Pi. These solutions are designed to work seamlessly even when your device is behind a router, ensuring you have uninterrupted access to your IoT setup.
1. Ngrok: The Ultimate Tunneling Tool
Ngrok is a popular tool used by developers to create secure tunnels for remote access. It’s super easy to set up and works great with Raspberry Pi. With Ngrok, you can expose your local server to the internet in just a few clicks.
How It Works:
- Install Ngrok on your Raspberry Pi.
- Run the command to create a tunnel.
- Access your device remotely using the generated URL.
Ngrok is a fantastic option for those who want a quick and easy solution without the hassle of configuring port forwarding.
2. Port Forwarding: The Classic Approach
Port forwarding is one of the oldest methods for enabling remote access to devices behind a router. While it requires a bit more effort to set up, it’s a reliable solution that works well for most use cases.
Steps to Configure Port Forwarding:
- Log in to your router’s admin panel.
- Locate the port forwarding section.
- Set up a rule to forward traffic to your Raspberry Pi’s IP address and port.
Keep in mind that port forwarding can expose your network to potential security risks, so it’s important to implement proper security measures.
Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT
Security should always be a top priority when setting up remote IoT devices. Here are some best practices to ensure your setup remains secure:
- Use Strong Passwords: Make sure all accounts and services are protected with strong, unique passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Add an extra layer of security by enabling two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system and applications to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Activity: Keep an eye on your network activity to detect any suspicious behavior.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your IoT devices.
Data Transmission and Protocols
When it comes to remote IoT, data transmission plays a crucial role. Choosing the right protocol can make a big difference in terms of performance and reliability. Here are some popular protocols used in remote IoT setups:
MQTT: Lightweight and Efficient
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight protocol designed for IoT applications. It’s perfect for devices with limited bandwidth and processing power, making it an ideal choice for Raspberry Pi.
Key Features of MQTT:
- Low Bandwidth Usage: Ideal for devices with limited connectivity.
- Publish/Subscribe Model: Allows for efficient communication between devices.
- Reliable: Ensures messages are delivered even in poor network conditions.
HTTP: Simple and Widely Supported
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a widely used protocol for web communication. While it may not be as efficient as MQTT, it’s simple to implement and works well for basic IoT applications.
Why Use HTTP:
- Easy to Set Up: No need for specialized libraries or tools.
- Universal Support: Compatible with most devices and platforms.
- Human-Readable: Makes debugging and troubleshooting easier.
Choosing the right protocol depends on your specific use case and requirements. Consider factors such as bandwidth, latency, and scalability when making your decision.
Dynamic DNS: Solving the IP Address Dilemma
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a great solution for dealing with dynamic IP addresses. It allows you to assign a static domain name to your device, even if its IP address changes. This makes it much easier to access your IoT setup remotely.
How DDNS Works:
- Register for a DDNS service provider.
- Install the DDNS client on your Raspberry Pi.
- Access your device using the assigned domain name.
Some popular DDNS services include No-IP, DynDNS, and DuckDNS. Each offers its own set of features and pricing plans, so be sure to choose one that suits your needs.
Hardware Considerations for RemoteIoT
While software plays a critical role in remote IoT setups, hardware considerations should not be overlooked. Here are some factors to keep in mind when choosing hardware for your Raspberry Pi-based IoT project:
- Processing Power: Ensure your Raspberry Pi model has enough processing power to handle your application’s requirements.
- Storage: Consider the amount of storage needed for your project, especially if you plan to store large amounts of data.
- Connectivity: Choose a model with built-in Wi-Fi and Ethernet for seamless connectivity.
Investing in quality hardware can make a big difference in the performance and reliability of your IoT setup.
Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT
Remote IoT has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are a few examples:
Smart Home Automation
With remote IoT, you can control your smart home devices from anywhere in the world. Whether it’s adjusting the thermostat or turning on the lights, Raspberry Pi makes it all possible.
Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring is essential in industries such as healthcare and agriculture. By setting up Raspberry Pi-based sensors, you can monitor critical parameters like temperature, humidity, and air quality in real-time.
Industrial IoT
In the industrial sector, remote IoT is used for predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and process optimization. Raspberry Pi’s versatility makes it a great choice for these applications.
These are just a few examples of how remote IoT can be applied in real-world scenarios. The possibilities are endless, limited only by your imagination.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best-laid plans can encounter hiccups. Here are some common issues you might face when setting up remote IoT with Raspberry Pi, along with their solutions:
Connection Issues
Problem: Unable to connect to your Raspberry Pi remotely.
Solution: Check your router settings and ensure port forwarding is configured correctly. Also, verify that your Raspberry Pi’s IP address is static or use a DDNS service to simplify access.
Security Concerns
Problem: Worried about unauthorized access to your IoT devices.
Solution: Implement security best practices such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping your software updated.
Data Transmission Problems
Problem: Slow or unreliable data transmission.
Solution: Optimize your network settings and choose the right protocol for your application. Consider upgrading your hardware if necessary.
By addressing these issues proactively, you can ensure a smooth and hassle-free experience with your remote IoT setup.
Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up remote IoT behind a router using Raspberry Pi is not only possible but also highly rewarding. With the right tools, protocols, and security measures in place, you can create a robust and reliable IoT setup that meets your needs.
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this article, from understanding the basics of remote IoT to exploring advanced configurations. Remember to always prioritize security and choose solutions that align with your specific requirements.
So, what are you waiting for? Grab your Raspberry Pi and start building your dream IoT project today. And don’t forget to share your experience in the comments below. Your feedback is invaluable to us, and we’d love to hear how this guide has helped you on your IoT journey.
For more exciting content, be sure to check out our other articles on Raspberry Pi and IoT. Stay tuned for more updates and stay connected!
Table of Contents:
- Why Raspberry Pi is the King of RemoteIoT
- Understanding RemoteIoT Behind a Router
- Top RemoteIoT Solutions for Raspberry Pi
- Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT
- Data Transmission and Protocols
- Dynamic DNS: Solving the IP Address Dilemma
- Hardware Considerations for RemoteIoT
- Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion
Article Recommendations